Hookup Doc: Your Go-To Guide for All Things Dating
Explore the latest trends, tips, and advice in the world of dating and relationships.
Fairness 2.0: Are Smart Contracts Smarter Than Your Lawyer?
Explore how smart contracts challenge traditional legal systems. Are they the future of fairness or just a fad? Find out now!
Understanding Smart Contracts: The Future of Legal Agreements
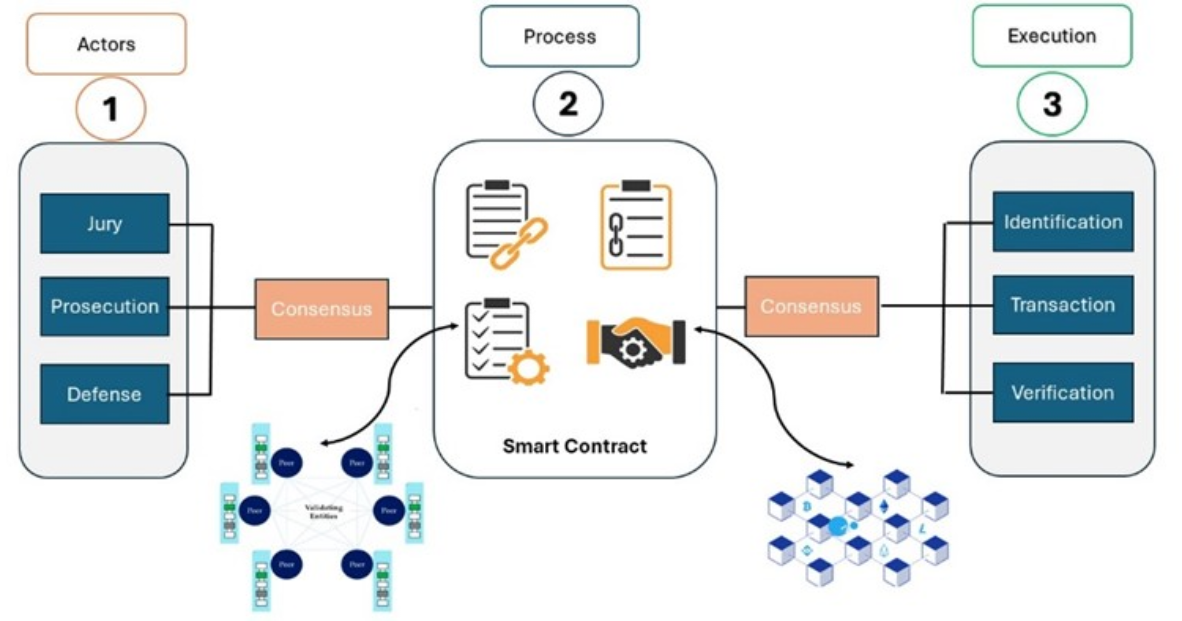
Understanding Smart Contracts is crucial in the digital age as they represent a revolutionary shift in how legal agreements are executed. These self-executing contracts, built on blockchain technology, automatically enforce and execute the terms of an agreement when predetermined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces the potential for disputes, and ensures transparency. Moreover, smart contracts are immutable, meaning that once deployed, their terms cannot be altered, providing a level of security and reliability that traditional agreements often lack.
As we delve into the future of legal agreements, it's important to consider the various applications of smart contracts across different sectors. For example, in real estate, they can streamline property transactions by automatically transferring ownership once payment is confirmed. In the financial industry, they can facilitate complex transactions and trading agreements without the need for middlemen. Overall, the adoption of smart contracts is expected to revolutionize how businesses and individuals approach legal agreements, enhancing efficiency and trust in contractual relationships.
Counter-Strike is a popular tactical first-person shooter game that has captivated millions of players worldwide. It emphasizes teamwork and strategy, where players can choose to be part of either the terrorist or counter-terrorist team. Many gamers also enjoy exploring various promotions and bonuses while playing, such as the bc.game promo code to enhance their gaming experience.
Smart Contracts vs. Traditional Legal Practices: Which Is More Reliable?
Smart contracts represent a breakthrough in the execution of contractual agreements, leveraging blockchain technology to automate processes and enforce terms without the need for intermediaries. They are self-executing contracts where the terms are directly written into code, ensuring that all parties fulfill their obligations transparently and securely. In contrast, traditional legal practices often rely on manual processes, negotiation, and intermediaries like lawyers and notaries, which can lead to delays and increased costs. As more businesses explore the capabilities of smart contracts, their efficiency and reliability are becoming increasingly appealing.
However, the question of reliability is nuanced. Traditional legal practices benefit from established frameworks, judicial oversight, and a nuanced understanding of human behavior and intention, which can be difficult to replicate in automated systems. Dispute resolution in traditional settings often involves mediation and litigation, whereas smart contracts can face challenges in complex scenarios where human judgment is required. Therefore, while smart contracts offer innovative solutions and enhanced efficiency, traditional legal practices provide a level of adaptability and trust that may be missing in automated systems, making the decision on reliability dependent on the context of use.
Can Smart Contracts Replace Lawyers in the Digital Age?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the digital age, smart contracts are emerging as a powerful alternative to traditional legal practices. These self-executing contracts are coded on blockchain technology, allowing for automatic enforcement of agreements without the need for intermediaries. This raises the question: can they truly replace lawyers? While smart contracts offer efficiency, transparency, and cost-effectiveness, the intricacies of legal systems involve human interpretation, context, and ethical considerations that are difficult to encode. Thus, while they can streamline many transactional processes, they may not completely supplant the nuanced roles that lawyers play in legal interpretation and dispute resolution.
Moreover, as smart contracts gain traction across various sectors, their integration within existing legal frameworks will require careful consideration. The benefits of automation and decreased transaction costs are compelling; however, this technology also poses challenges such as potential bugs in the code and the question of liability. Therefore, rather than completely replacing lawyers, smart contracts might serve as a complementary tool that can enhance legal practices. This partnership could redefine the role of lawyers, shifting their focus from contract execution to advisory services, ensuring compliance, and navigating the complexities of law in a digitized world.